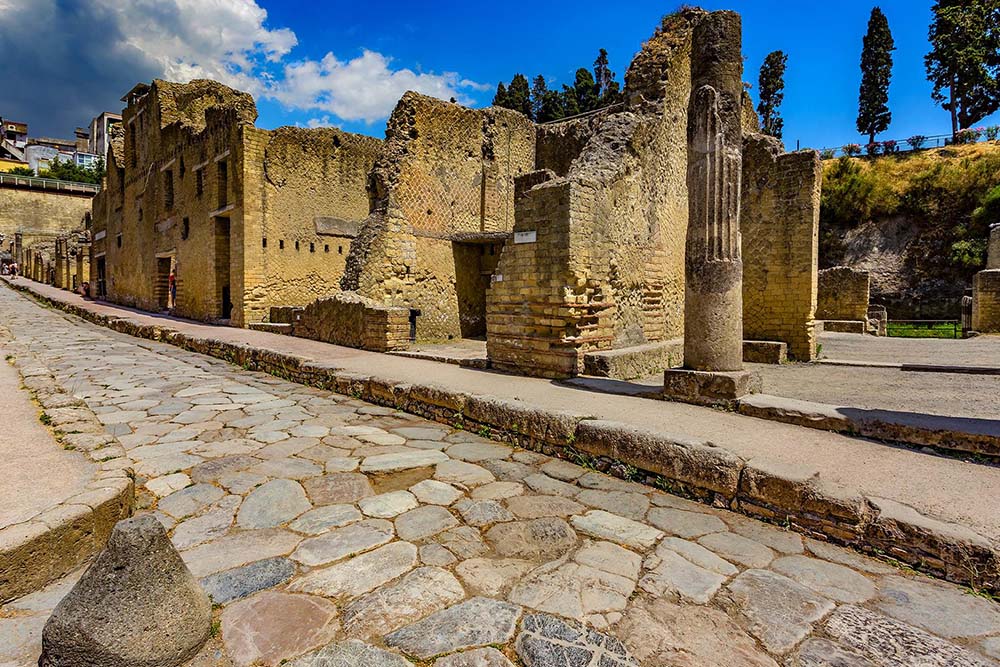
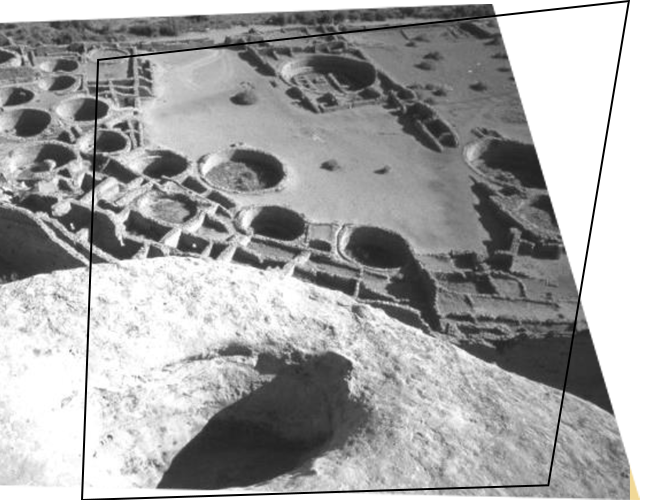
The popular image of archaeology seems to be of treasure hunters or dusty professors commanding an army of laborers in the excavation of a lost civilization in a strange and exotic land. That sounds exciting, but it is not exactly accurate. Perhaps we should start with what archaeology is not. It is not “Indiana Jones” or “Tomb Raider,” and it is not pot hunting or grave robbing. None of that is science. It is not geology, the study of the earth and its mineral components, and it is not paleontology, the study of plant and animal fossil remains. Although these are also scientific disciplines, and archaeologists do sometimes deal with rocks and fossils, they are not archaeology.
So what is archaeology?
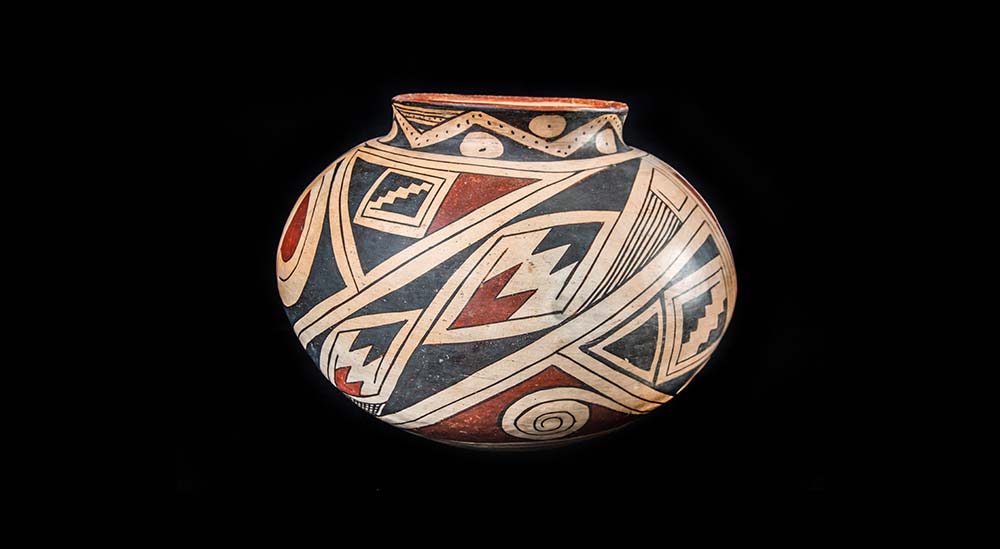
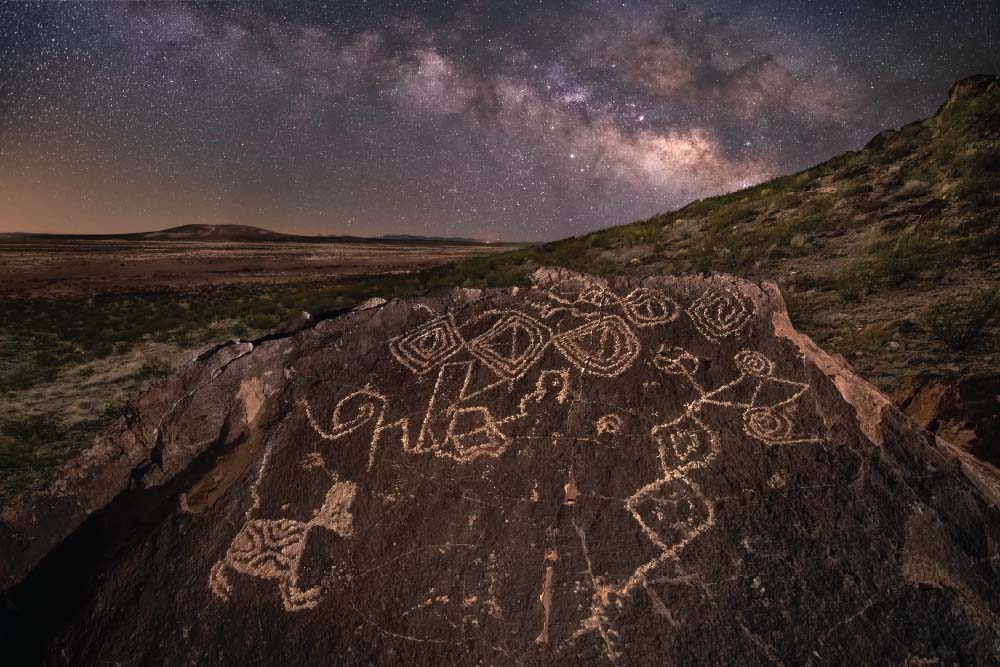
Archaeology is the study of cultures that lived in the past. It is a subfield of anthropology, the study of human cultures. The other subfields are cultural anthropology that studies living cultures, physical anthropology that studies human biology and where humans fit among the living and extinct species of our family tree, and linguistics that studies human language. Archaeology is primarily concerned with reconstructing extinct cultures from the material remains of past human behavior, or the things people made or used and left behind. These remains are called artifacts. Much of what we see around us – computers, clothing, food, books, and buildings – are artifacts. Even natural objects, like a stick of wood or a piece of bone, are artifacts if humans have used them for some purpose.